SoFiA
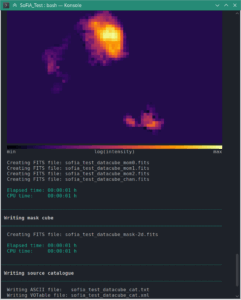
The Source Finding Application, SoFiA, is a new, fully automated source finding and parameterisation pipeline for 3-D extragalactic HI data cubes developed as part of the activities of WALLABY’s technical working group 4 (“Source finding and cataloguing”) led by Tobias Westmeier. SoFiA combines a large number of sophisticated algorithms, allowing users to choose an optimal set of parameters for their specific data cube. In addition to the command-line tool, SoFiA also comes with a modern graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to interactively change the pipeline settings, run the pipeline from within the GUI, and inspect the resulting output catalogues and images. SoFiA will continue to be developed and improved by our team and has been made available to the community via GitLab.
- SoFiA on GitLab
- SoFiA wiki with tutorials and documentation
- Support packages for SoFiA:
- Optional Graphical User Interface for SoFiA
- OptiFind allows SoFiA to be run on small subregions around optical sources
- BusyFit can be used to fit a Busy Function to the integrated HI spectra of galaxies
- Plotting tools such as SIP (see below) and SpecPlot
- SoFiA description papers:
2DBAT
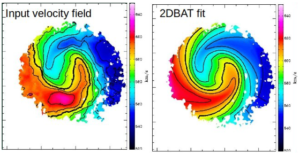
The 2-D Bayesian Automated Tilted-ring fitter, 2DBAT, has been developed by Se-Heon Oh and the WALLABY Kinematics working group for the purpose of fitting tilted rings to the 2-D velocity field of spatially resolved galaxies detected by the WALLABY survey and extract their rotation curves. By using a new Bayesian-based algorithm instead of the standard χ2 minimisation, the fitting procedure is more robust and can be fully automated, which is crucial for fitting the large number of extended galaxies expected to be detected by WALLABY. 2DBAT works best for well-resolved galaxies with intermediate inclinations in the range of 20° < i < 70°, complementing 3-D techniques better suited to modelling highly inclined galaxies. 2DBAT has been made available to the community via GitHub.
- 2DBAT on GitHub
- 2DBAT overview paper: Oh, S.-H., Staveley-Smith, L., Spekkens, K., et al., 2018, MNRAS, 473, 3256 (ADS | arXiv)
FAT
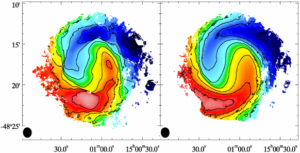
Fully Automated TiRiFiC, FAT, is a wrapper around the Tilted Ring Fitting Code (TiRiFiC) which aims to fully automate the process of fitting simple tilted ring models to spectral line emission cubes of resolved galaxies. Developed by Peter Kamphuis and the WALLABY Kinematics working group, FAT fits simple rotationally symmetric discs with asymmetric warps and surface brightness distributions in order to extract the rotation curve of the galaxy. FAT accurately models the kinematics and morphology of galaxies with an size of eight beams across the major axis and in the inclination range of 20° < i < 90° without the need for priors. This will allow the large number of well-resolved galaxies that WALLABY will detect to be fitted in an automated fashion. FAT has been made available to the community via GitHub.
- FAT on GitHub
- FAT overview paper: Kamphuis, P., Józsa, G. I. G., Oh, S.-H., et al., 2015, MNRAS, 452, 3139 (ADS | arXiv)
SIP
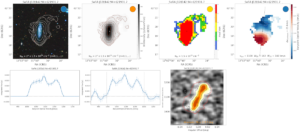
The SoFiA Image Pipeline (SIP) is a tool for generating publication-ready plots based on the output from SoFiA. The development of SIP is led by Kelley Hess. SIP is capable of generating plots of moment maps, multi-wavelength images with HI column density contours, integrated spectra, position–velocity diagrams and many more. It is particularly useful for the automatic generation of overview plots for visual inspection and assessment of source finding runs on large surveys.
- SIP on GitHub
3KIDNAS
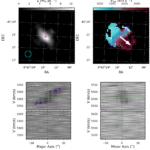
The 3d Kinematic Data aNalysis Algorithm for Surveys (3KIDNAS; pronounced /ɪˈkɪdnəz/) is an automated kinematic pipeline that produces kinematic models of rotating disk galaxies with robust and statistically meaningful uncertainties. The pipeline is being developed by WALLABY’s technical working group 5 under the leadership of Kristine Spekkens and Nathan Deg. 3KIDNAS will be used to eventually model the kinematics and rotation curves of several thousand spatially resolved galaxies detected by the WALLABY survey in the nearby Universe. While still under active development, a preliminary version of the pipeline has already been made available to the public via GitHub.
- 3KIDNAS on GitHub
Other WALLABY software packages
SoFiA–X
SoFiA–X is a parallel wrapper around SoFiA 2 that allows source finding to be carried out on smaller regions of a large data cube in parallel across multiple compute nodes. It will write the SoFiA output into a shared database and can be set up to automatically remove duplicate detections in regions of overlap between two nodes. SoFiA–X was developed by the Australian SKA Regional Centre (AusSRC) as part of their WALLABY support.
- SoFiA–X on GitHub
- SoFiA–X support packages:
- SoFiA–X Services for database & web interface setup
- S2P Setup for creating SoFiA and SoFiA–X configuration files
- SoFiA–X description paper: Westmeier, T., Kitaeff, S., Pallot, D., et al., 2021, MNRAS, 506, 3962 (ADS | arXiv)
WALLABY Pipelines
The AusSRC has developed a set of post-processing pipelines and data access repositories for the WALLABY survey which are available on GitHub. These pipelines are used to carry out source finding and quality control on the WALLABY survey and provide ways of storing and accessing value-added data products.
External resources
In addition to the software tools developed by the WALLABY team, the following external software packages and computing projects are of relevance to WALLABY.
- AusSRC GitHub site
- ATNF GitHub site
- ASKAPsoft documentation
- Duchamp source finder by Matthew Whiting



